How to use our Library¶
We use a simple example to illustrate how to use our library. Below is an undirected graph with three nodes.
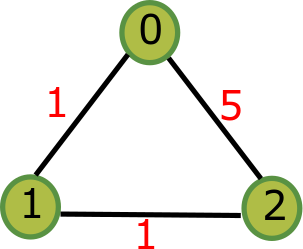
From theory it has a hierarchical clustering structure like this one:
/-0
/-|
--| \-2
|
\-1
C++ User¶
After installation of C++ library, in your C++ code, you use our library in the following way:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | #include <iostream>
#include <tuple>
#include <vector>
#include <psp/psp.h>
int main() {
std::vector<std::tuple<std::size_t, std::size_t, double>> arc_list;
// construct the example graph
arc_list.push_back(std::make_tuple(0, 1, 1.0));
arc_list.push_back(std::make_tuple(0, 2, 5.0));
arc_list.push_back(std::make_tuple(1, 2, 1.0));
// construct the algorithm class instance
psp::PSP psp_instance(arc_list, 3);
psp_instance.run();
std::vector<double> critical_values = psp_instance.get_critical_values();
std::vector<stl::Partition> partition_list = psp_instance.get_partitions();
// process the results
std::vector<double>::iterator critical_values_iterator = critical_values.begin();
std::vector<psp::Partition>::iterator partition_list_iterator = partition_list.begin();
for(; critical_values_iterator != critical_values.end(); critical_values_iterator++) {
std::cout << *partition_list_iterator << std::endl;
std::cout << *critical_values_iterator << std::endl;
partition_list_iterator++;
}
std::cout << *partition_list_iterator << std::endl;
}
|
First you include our header file, which provides our algorithm class PSP and data structure Partition.
Then you prepare the input data, which requires a std::vector whose elements are std::tuple.
For each tuple \((i,j,w)\), it represents the first node index, the second node index and the edge weight
between the two nodes. The second parameter to construct PSP is the number of nodes in your graph.
Next you run the algorithm by invoking the public method run of PSP. Finally you get the critical values
and partitions results.
Python User¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | a = [[0,1,1], [0,2,5], [1,2,1]] # a graph
p = PsPartition(3, a) # 3 nodes
p.run()
cv = p.get_critical_values()
pl = p.get_partitions()
print(cv)
print(pl)
|
First you prepare a Python list and each element contains (source_node, destination_node, weight) information. Next you construct the algorithm class and pass your graph data to it. Then you run the algorithm with default implementation. Finally you get the critical values and partitions results.